Did you know that fat distribution in your body reveals a lot about your health and eating habits? Fat plays a vital role in providing energy, supporting organ functions, and regulating body temperature. However, the accumulation of visceral fat (surrounding internal organs) or subcutaneous fat may indicate unbalanced eating habits or an unhealthy lifestyle.
In this article, we will explain the types of body fat and their meanings, such as triglycerides, monounsaturated fats, and bad cholesterol. We will also provide recipes to balance fat intake, whether saturated or trans fats, and avoid the risks associated with them. Remember, fat is not just extra weight; it is the result of interactions between hormonal, psychological, and physical activity factors. Each type of fat, whether visceral or subcutaneous, carries a different message about your health!
Fat in the body is not just a matter of excess weight; it is distributed in different ways depending on eating habits, physical activity (energy balance and health), and hormonal and psychological factors. There are several types of fat that accumulate in the body, each with its own significance and importance:
1. Full Upper Body Fat
- Cause: Excessive consumption of sugar, carbohydrates, and oils (high-calorie intake).
- Appearance: Fat accumulation in the arms, back, abdomen, and chest.
- Meaning: Usually results from consuming large amounts of refined sugar and carbohydrates.
- Solution: Reduce sugar intake and increase protein and fiber consumption.
2. Lower Abdominal Fat
- Cause: Chronic stress and increased cortisol levels.
- Appearance: Fat is concentrated only in the lower abdomen, below the navel.
- Meaning: Often linked to chronic stress and high cortisol levels.
- Solution: Practice relaxation exercises, walking, and ensure quality sleep.
3. Large Abdominal Fat
- Cause: Lack of physical activity.
- Appearance: General bloating in the abdomen and increased waist size.
- Meaning: Typically results from a sedentary lifestyle.
- Solution: Increase physical activity, such as walking and high-intensity workouts.
4. Lower Body Fat
- Cause: Excessive gluten consumption.
- Appearance: Fat accumulation in the hips and thighs.
- Meaning: May be linked to metabolic disorders or high gluten intake.
- Solution: Reduce gluten consumption and focus on lower-body exercises.
5. Bloated Belly Fat
- Cause: Poor nutrition and excessive processed food consumption.
- Appearance: A protruding and bloated stomach without significant weight gain in the rest of the body.
- Meaning: Often associated with poor nutrition and high intake of processed foods.
- Solution: Eat natural foods and reduce consumption of processed and fried foods.
Ways to Maintain Fat Balance in the Body
- Balanced Nutrition: Consume proteins, fibers, and healthy fats while reducing sugar intake.
- Physical Activity: Engage in daily walking, strength training, and cardio exercises.
- Stress Management: Improve sleep quality, practice relaxation techniques, and reduce anxiety.
- Reduce Processed Foods: They contribute to fat accumulation in specific areas of the body.
Best Recipes to Maintain Fat Balance in the Body
1. Avocado and Chickpea Salad
Why? Avocado is rich in healthy fats that help balance cholesterol levels, and chickpeas are an excellent source of fiber that reduces the absorption of harmful fats.
2. Broccoli Soup
Why? Contains antioxidants that boost metabolism and help reduce belly fat accumulation.
3. Stuffed Shell Pasta with Spinach and Ricotta Cheese
Why? Provides protein from cheese and vitamins from spinach, helping build muscle and burn fat healthily.
4. Healthy Stewed Lentils
Why? Lentils are rich in fiber and protein, promoting satiety and reducing cravings for unhealthy fatty foods.
5. Tuna Salad
Why? Tuna is a rich source of Omega-3, which helps improve triglyceride levels and reduce inflammation.
6. Healthy Oat Bread
Why? Oats are an excellent source of fiber that aids digestion and reduces the absorption of unhealthy fats.
7. Energy Balls with Dates and Almonds
Why? Provide sustainable energy without processed sugars, helping reduce upper body fat.
8. Broccoli Omelet Recipe
Why? Eggs are high in protein, and broccoli contains fiber and antioxidants that help reduce bloated belly fat.
9. Brown Lentil Rice with Salad and Sauce
Why? A combination of complex carbohydrates and proteins that help regulate blood sugar levels and reduce unhealthy fat accumulation.
10. Healthy Carrot Cupcakes
Why? A good source of fiber and beta-carotene, promoting skin health and reducing fat-related inflammation.
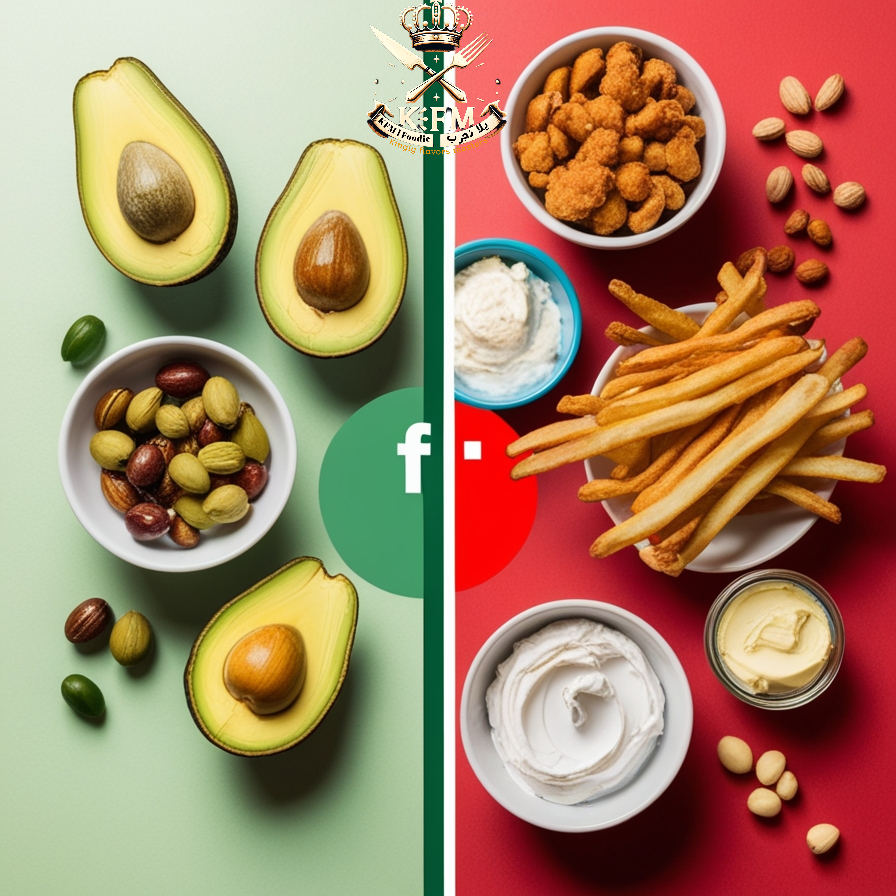

Additional Tips for Managing Body Fat
- Drink Plenty of Water: Helps flush out toxins and excess fat. Water also boosts metabolism and reduces fluid retention.
- Portion Control: Eating moderate amounts prevents fat storage.
- Do Cardio Exercises: Activities like brisk walking or running help burn excess fat. (Combining strength training with cardio helps eliminate accumulated fat.)
- Avoid Processed Foods: Such as commercial baked goods and fast food. (Avoiding processed and fried foods helps reduce belly fat.)
- Get Enough Sleep: Lack of sleep increases cortisol levels, which promotes fat storage.
- Manage Stress: Meditation, walking, and breathing exercises help lower stress levels and prevent fat gain.
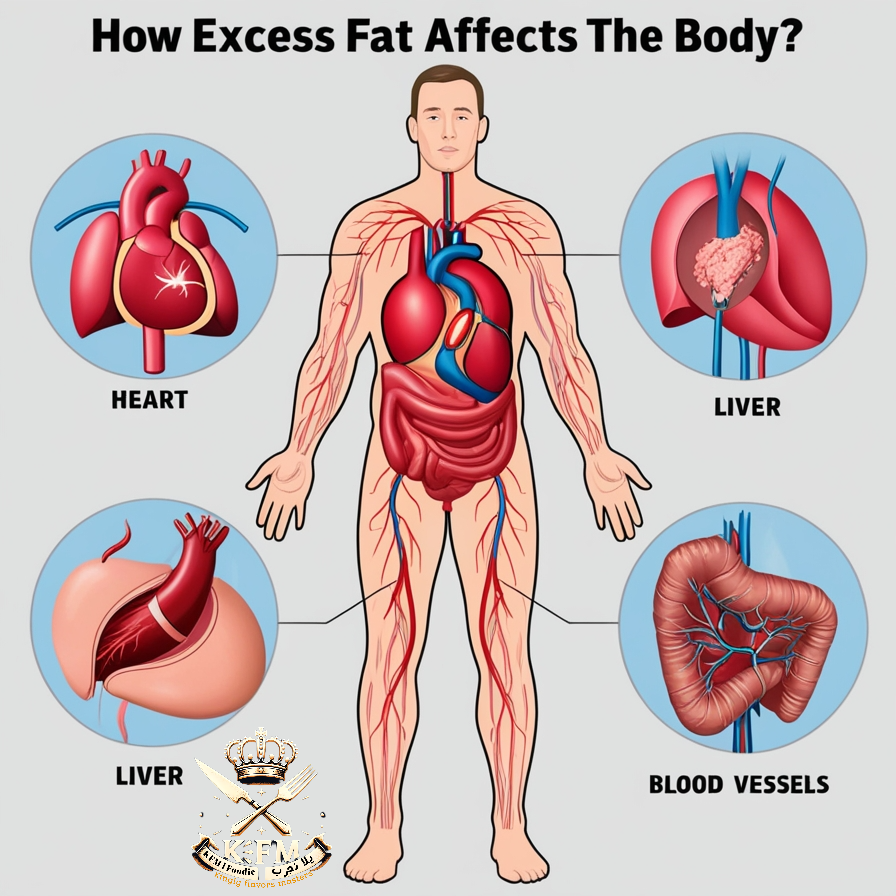
The Difference Between Healthy and Unhealthy Fats
Fats are an essential part of the diet, but not all fats are equal in terms of benefits or harm. They can be classified into:
🔹 Healthy Fats (Unsaturated):
- Found in plant-based oils such as olive oil and canola oil.
- Present in nuts, avocados, and seeds.
- Improve heart health and reduce bad cholesterol (LDL) levels.
🔹 Unhealthy Fats (Saturated and Trans Fats):
- Saturated Fats: Found in red meat, butter, and full-fat dairy products like white cheese.
- Trans Fats: Found in fried foods and processed baked goods.
- Increase the risk of heart disease and raise bad cholesterol levels.
The Role of Hormones in Fat Storage
Hormones play a significant role in regulating body fat. Some of the most important hormones include:
🔸 Insulin:
- Secreted by the pancreas in response to high blood sugar levels.
- Consuming large amounts of sugars and simple carbohydrates increases insulin, leading to fat storage instead of burning.
🔸 Cortisol (Stress Hormone):
- Stimulates fat storage, especially in the abdominal area.
- Chronic stress increases cortisol secretion, leading to visceral fat accumulation.
🔸 Estrogen:
- In women, estrogen helps store fat in the hips and thighs.
- Its decline after menopause leads to fat accumulation in the abdominal area.
Frequently Asked Questions
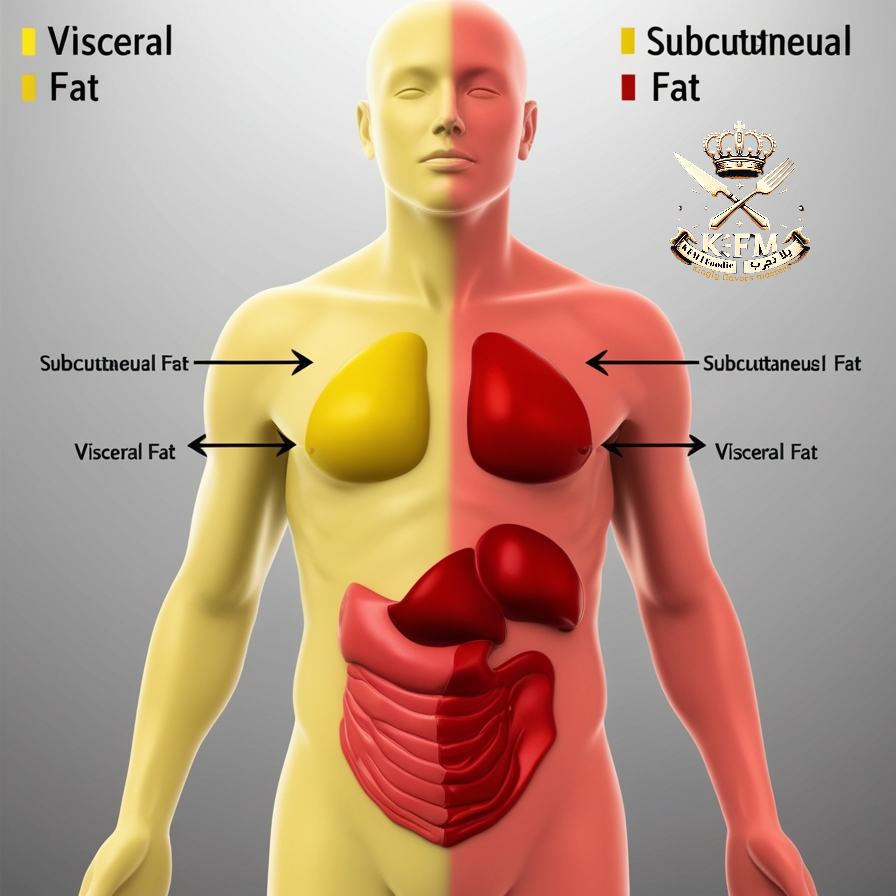
What is the difference between visceral fat and subcutaneous fat?
- Visceral fat: Accumulates around internal organs such as the liver and intestines, increasing the risk of diabetes and heart disease.
- Subcutaneous fat: Located just beneath the skin’s surface. It is less dangerous than visceral fat but can affect physical appearance.
How can I determine my body fat type?
You can identify it using body composition analysis devices like InBody or through ultrasound examination.
Visceral fat is measured by waist circumference, with a measurement greater than 102 cm (40 inches) for men and 88 cm (35 inches) for women indicating high visceral fat levels.
Can I lose fat from specific areas like the waist and belly?
It is not possible to target fat loss in a specific area. However, overall fat loss through diet and exercise will gradually reduce fat in targeted areas.
What is the best diet for fat burning?
Balanced diets that include proteins, fiber, and healthy fats while reducing sugars and refined carbohydrates are effective.
Diets such as keto or low-carb may help some people lose fat faster.
How long does it take to lose excess body fat?
It depends on factors such as diet, physical activity, and genetics.
A healthy weight loss rate is 0.5 to 1 kg (1 to 2 lbs) per week, ensuring sustainable results without negatively affecting health.
Conclusion:
Achieving a healthy fat balance in your body starts with choosing foods rich in healthy fats, such as essential fatty acids (like Omega-3 in fish) while avoiding harmful trans fats and excessive saturated fats.
Start your journey today by applying these tips:
✔️ Do cardio exercises to burn visceral fat.
✔️ Choose olive oil instead of hydrogenated oils.
✔️ Consult a nutritionist to monitor bad cholesterol and triglyceride levels.
🔴 Remember: Moderation in fat intake, stress management, quality sleep, and avoiding high-calorie, energy-dense foods like peanuts are your weapons against subcutaneous fat accumulation and for maintaining a healthy heart!
💡 Save this article for later! ❤️ Comment if you found this information useful! 🔄 Share it with friends to spread the knowledge!