Food drying is an ancient process used to preserve food for long periods without the need for refrigeration or freezing. This method is ideal for maintaining the nutritional content and natural taste of foods, and it provides a practical way to store large quantities of food. There are several methods of food drying, such as sun drying, air drying, or using modern food dehydrators. In this article, we will explore the most important available methods for drying foods and explain how to implement each one effectively to achieve the best results in preservation.
Natural Drying
Principle of Natural Drying
Explanation of the natural drying process using direct sunlight or hot air in shaded areas.
Benefits of Natural Drying
- Long shelf life and sustainability.
- Ease of transportation and distribution.
- Concentration of nutritional value in dried foods.
Disadvantages of Natural Drying
- Exposure of dried materials to dust and insects.
- Sensitivity of some ingredients to light.
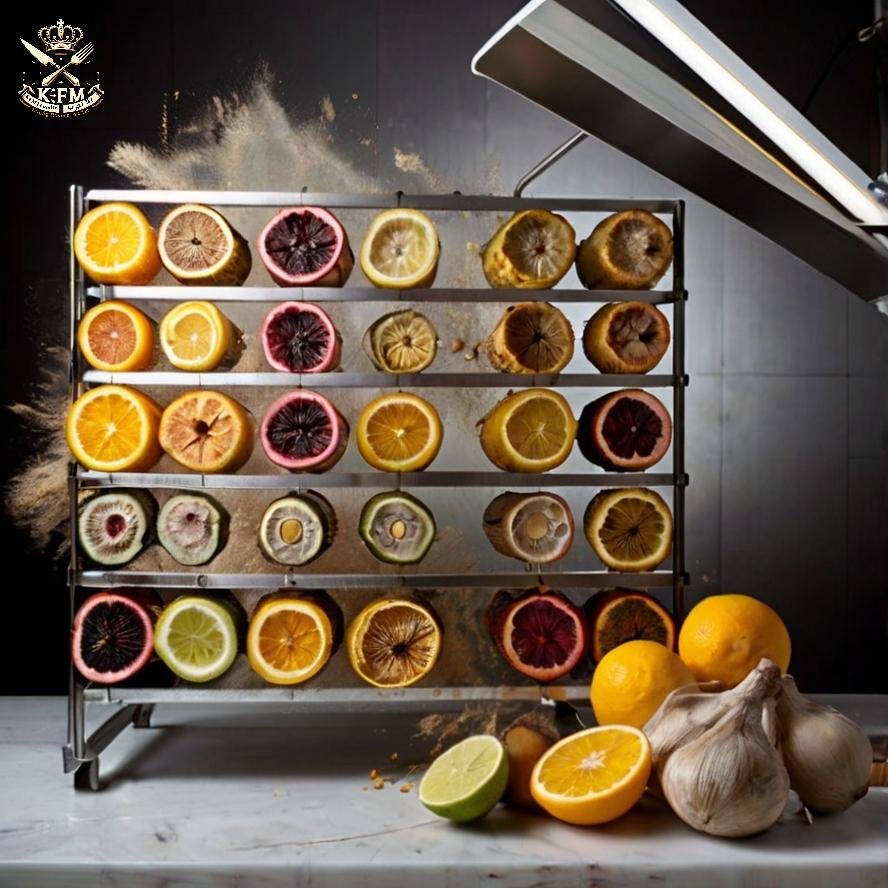

Artificial Drying
Principle of Artificial Drying
Explanation of the drying process using machines specifically designed for heat, including electric and gas-powered devices.
Benefits of Artificial Drying
- High quality of the dried product.
- Precise control of temperature and distribution within the device.
Disadvantages of Artificial Drying
- High costs due to electricity consumption.
- Risk of leaks and potential issues with gas-powered devices.
Conclusion: Emphasizing the importance of drying as an effective and crucial method for food preservation, with a focus on the importance of choosing the appropriate method based on circumstances and needs.